Knowledge in one place.
By Tatiane Figueiredo – Training Instructor
More and more Internet providers need to aggregate and deliver, to end customers, services that involve access to videos on demand, cloud applications, interactive content on digital platforms, in addition to the increase in mobile devices such as smartphones, tablets and laptops accessing the Internet. Another growing factor is the Internet of Things - IoT, with external access to sensors, lamps, coffee makers, cameras and others.
One of the technologies that has driven this growth is the GPON - Gigabit Passive Optical Network, which allows you to take optical fiber to the last mile of the network.
As already discussed in our blog (See 16-port OLT article, Power budget, among others), designing an optical network requires a lot of care. One of the important points that providers must foresee in the optimization of service coverage, is how the geographical distribution of OLTs and optical access networks will be made.
In another article on the blog about our 16-port standalone OLT (DM4615), we present an analysis on which type of OLT to choose to build a GPON network, that is, it is more advantageous to choose a large modular OLT and form centralized networks , or choose small / medium-sized OLTs and form decentralized networks?
Many providers prioritize port density and, therefore, opt for modular equipment, which has a high initial investment cost and sometimes ends up being underutilized. DATACOM believes that the decentralization of GPON networks is a cost-effective option, because in addition to allowing more optimized coverage, it also brings greater resilience to the ISP.
See below the advantages of using Standalone OLTs and focus on decentralized networks:
1. Reduction of physical space
The provider must plan where the GPON network will be the focal point, that is, where the OLT that will connect its subscribers will be installed. In addition to simplifying installation, depending on the situation, the physical space occupied by the OLT in the rack can have a significant impact on the cost of the project, because many times the point of presence (PoP) chosen by the ISP is from a third party and it is necessary to contract co-location to assemble the GPON structure.
Standalone OLTs reduce the demand for physical space, as they occupy only 1U of height in the POPs' rack structures or in shelters installed externally (street, condominium and power poles).
The following figure illustrates the space occupied by an OLT of 6Us, 11Us and 1Us, for indoor (Rack 19 ') and outdoor (Rack Telecom Outdoor) environments.
2. Reduced downtime due to firmware update
We observe on a daily basis that the firmware update procedure is something that causes concern to technicians and network administrators.
Updating the firmware of an OLT that operates in a centralized way, with several GPON cards, demands a lot of attention to perform the procedure and also has a high downtime due to the need to reboot the equipment. This action can leave 2,000, 4,000 or more clients out of operation for several minutes, until the equipment reboots and all PPPoE sessions are authenticated.
With the operation of a standalone OLT, the criticality of the update is reduced, since the network is segmented and the downtime by reboot is much less. The procedure is easier and faster, because, among other things, the upgrade does not involve updating individual boards for example. Even the maintenance window time can be reduced by choosing to work with decentralized architecture.
3. Less energy problems
A critical point commented on by the providers is the inconvenience caused by problems with the supply of electricity, with the use of pizzabox equipment the need for nobreaks and batteries to maintain minimum autonomy is reduced compared to the centralized solution.
With the decentralization of the equipment, the cooling process is also reduced due to its lower energy consumption, including one of the characteristics of this model is its installation in places with the highest operating temperature, such as in outdoor cabinets / racks or in a shelter . In addition, there are GPON modules for extended temperatures, facilitating and operationalizing this type of topology.
4. Network segmentation using Metro Ethernet resources
Building and planning a decentralized topology, with pizzabox OLTs, brings to the provider greater reliability of the services and of its own network, since there will be several concentrators for authentication of the clients, without counting on the use of layer 2 protocols such as Rapid Spanning- Tree and EAPS - Ethernet Automatic Protection Switching that guarantee redundancy and fast convergence of applications made available to customers. Other features can also be configured to provide greater availability, such as the use of LAG (link-aggregation), routing and even transport with the MPLS protocol (see article on the blog “Explore the switching features of your OLT”).
5. Ease of analyzing possible failures
Of course, no solution is 100% fail-safe, neither centralized nor decentralized, but by dividing our network, our problems are also minimized, be they configuration or hardware. Imagine the negative impact of those who centralized their entire network and are having problems with the core? Today, access to the Internet is as essential as water and energy.
6. Flexibility in providing access to customers
Another point that we can highlight are the applications that the standalone model can be incorporated:
7. More simplified passive networks
Planning the arrival of the fiber considering a single distribution point poses a great challenge. The active equipment closest to its customers allows a more optimized planning of the GPON network, including improving the power level (dBm) received at the UN WAN port - Optical Network Unit, which will reflect in the power budget of your network.
In addition, a well-planned network with decentralized distribution will bring savings in terms of the launch of fiber optics, which has a high impact cost on the project.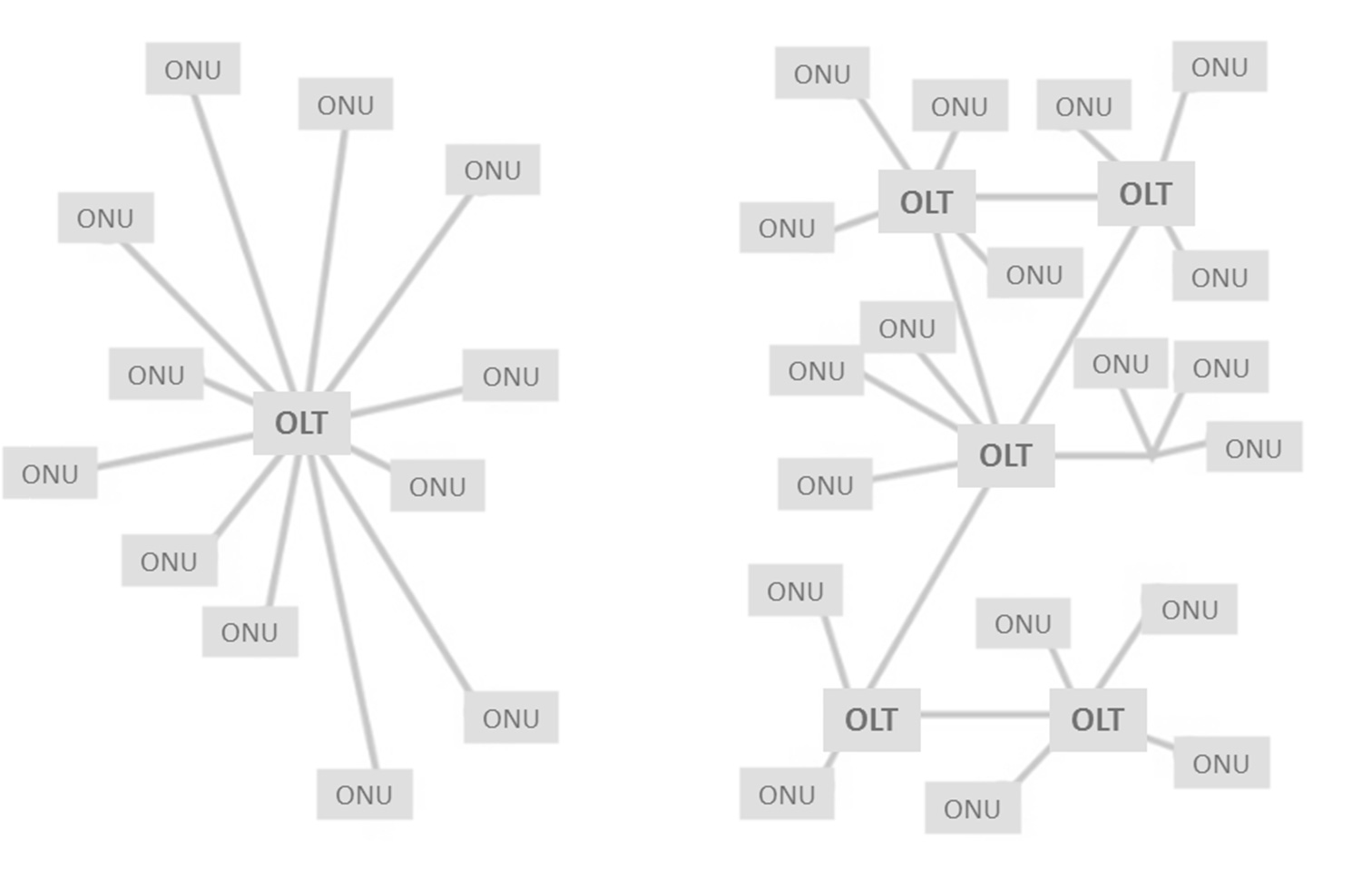
Among the pizzabox OLT models, Datacom offers equipment with 4, 8 and 16 GPON ports, all with 1Gbps and 10Gbps Ethernet ports, for interconnection with the transport network.
DATACOM OLTs use the DmOS operating system, which adds in addition to GPON features, a complete ethernet metro featureset, including L2, L3 and MPLS features.
In addition, DmOS is a scalable and constantly evolving software platform, which allows customers who use it to benefit from this evolution to the limit of their hardware capacity.
Always remembering that Datacom has a complete structure in its headquarters, where face-to-face training is conducted. In the training it will be possible to manipulate the equipment, perform configurations of different topologies and application scenarios in a complete laboratory environment, in addition to being able to count on the help of our professionals in a series of good practices that will greatly assist in the operation of your network.
For questions and request for proposal, contact Datacom's commercial team: sales@datacom.com.br ou (+55) 51 3933 3000.
If you have questions about these applications, Datacom makes its support team available: suporte.prevendas@datacom.com.br. We are available to assist you in choosing the product that best suits your needs.
* This feature is available on DATACOM OLTs and is defined by ITU-T G984.7 (Long Reach).