The DM984 GPON ONU (optical network unit) family offers high speed fiber optic access solution. They deliver triple-play services (data, voice and video over IP) for business and residential users. The ethernet data is transported transparently by the GPON link and delivered to a optical line termination (OLT), as the DM4610 OLT.
It has the ability to add, remove and modify VLANs. Supports QoS and multicast traffic for video transport.
POWER SUPPLY
ENVIRONMENT DATA
GPON
Ethernet
FXS interface (VoIP)
Router
Wireless (WI-FI)
Triple Play Broadband Services
Through optical access, GPON technology allow convergence of data, voice (VoIP) and video (IPTV) in a single access.
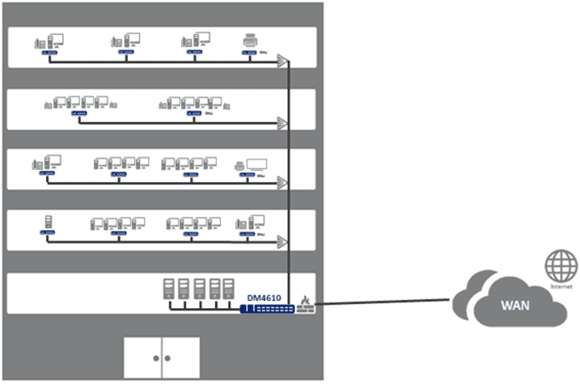
Business services
The DM4610 provides a number of features that enable data, voice and video delivery to small, medium and large businesses.
The TLS (Transparent LAN Service) feature together with the Hairpin feature allows you to offer LAN-to-LAN services without additional equipment - such as routers.


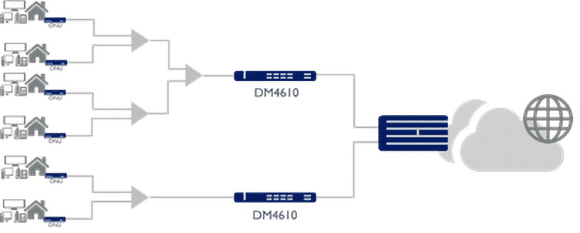
FTTD – Fiber to the Desk
GPON FTTD simplifies the network by replacing the switches typically by a central OLT and ONUs in the users, reducing the network infrastructure using passive elements, fiber optics and point-multipoint topology.